Configuration by Web Page
This page presents capabilities of configuration modbus gateways. At the beginning, make sure that gateway is connected to power supply and to the LAN using the patch cord. User interface is mostly similar for every gateways but some subpages might be diffrent for several models depends on amount of interfaces. In order to avoid some issues, click on a Help button in the top right corner on every page.
Login
To access the web page open the browser, type IP address of the converter (default is 192.168.100.100). Then log in using your personal credentials unless it is a first configuration or converter had factory reset, then use default login details.

Login panel on web page
Configuration is available only if devices are connected to the same Local Area Network as the computer you are using.
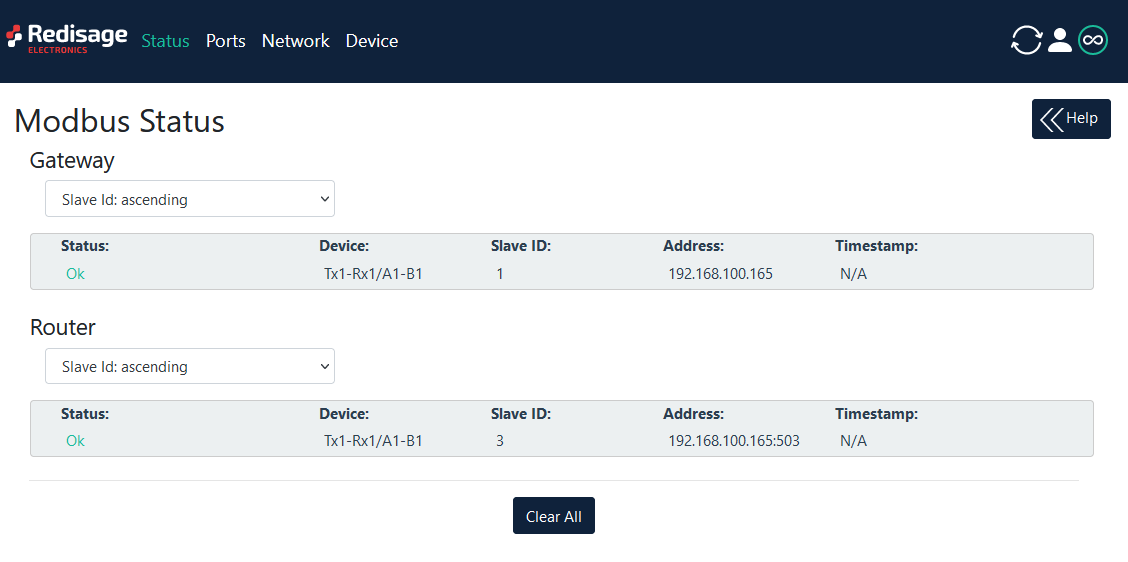
Status page
After successful login, you have insight to list of available connections. In case of more connection, you can sort them by ID, timestamp or status.
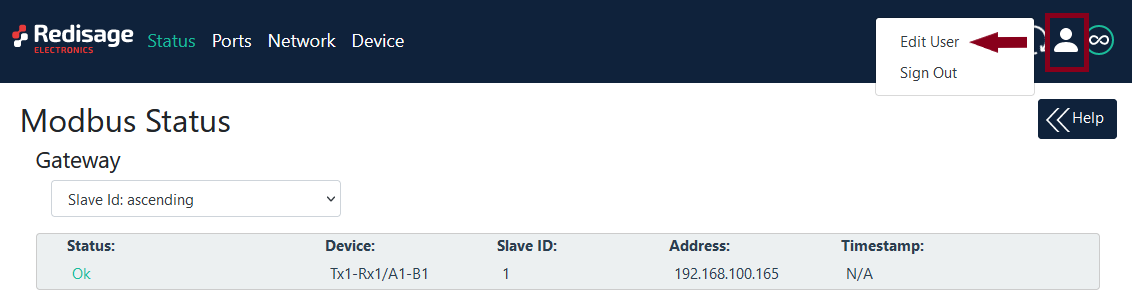
Changing username or password
To change your username or password you have to click on user icon and then Edit User.
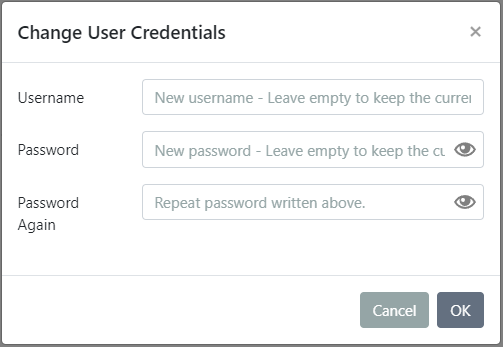
In the next step you will be able to change user credentials up to your preferences.
If you forgot your login details, all you can do is factory reset via USB/UART converter and serial console.
Ports configuration
This page allows to configure ports.
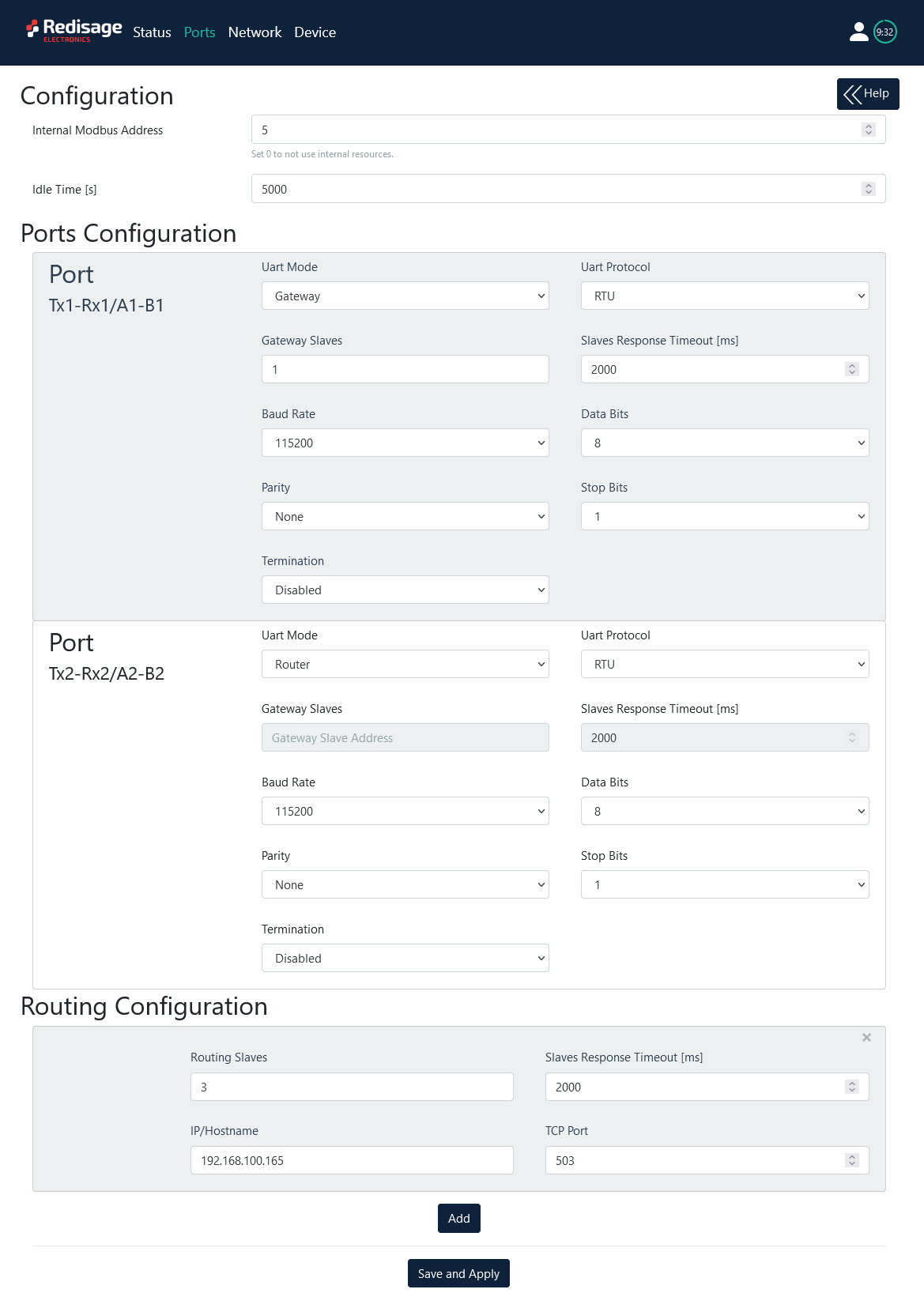
Ports configuration
Item | Description | |
|---|---|---|
Internal Modbus Address | Internal Modbus Address is qualified by Gateway/Router as a request for internal resources. Internal Modbus Address has a higher priority than Gateway Slave Address. | |
Idle Time [s] | Determines the time thread waits for the TCP connection. If time expired, the connection and thread are closed. Used only in Gateway Mode. | |
UART Mode | Gateway | Defines the port's role in the system. In Gateway Mode port is used to communicate with Modbus Slave. |
Router | Defines the port's role in the system. In Router Mode port is used to communicate with Modbus Master. Note the Routing Configuration section below if Router Mode is chosen. | |
UART Protocol | Determines protocol used to communication. | |
Gateway Slaves | Addresses of Modbus Slave Devices connected to Gateway UART ports. Multiple addresses can be written in one field, e.g. 9;11;14-17;80. This field is available only in Gateway Mode. Use * to select all not assigned addresses. | |
Slaves Response Timeout [ms] | Specifies how long the Device will wait for response from Modbus Slave. | |
Baud rate | Determines the port's transmission speed over the data channel. | |
Data Bits | Determines the number of data bits in the port's message frame. | |
Parity | Enables/disables parity check in the port's message frame. | |
Stop Bits | Determine the number of stop bits in the port's message frame. | |
Termination | Enables/disables termination on RS line. | |
Routing Slaves | Addresses of Modbus Slaves connected to Modbus Router. Multiple addresses can be written in one field, e.g. 9;11;14-17;80. Use * to select all not assigned addresses. | |
Slaves Response Timeout [ms] | Specifies how long the Device will wait for response from Modbus Slave. | |
IP/Hostname | Determines IP address or Hostname of Modbus Slave. | |
TCP Port | Determines TCP port of Modbus Slave. | |
Network settings
In this section, network settings can be changed according to target LAN parameters.
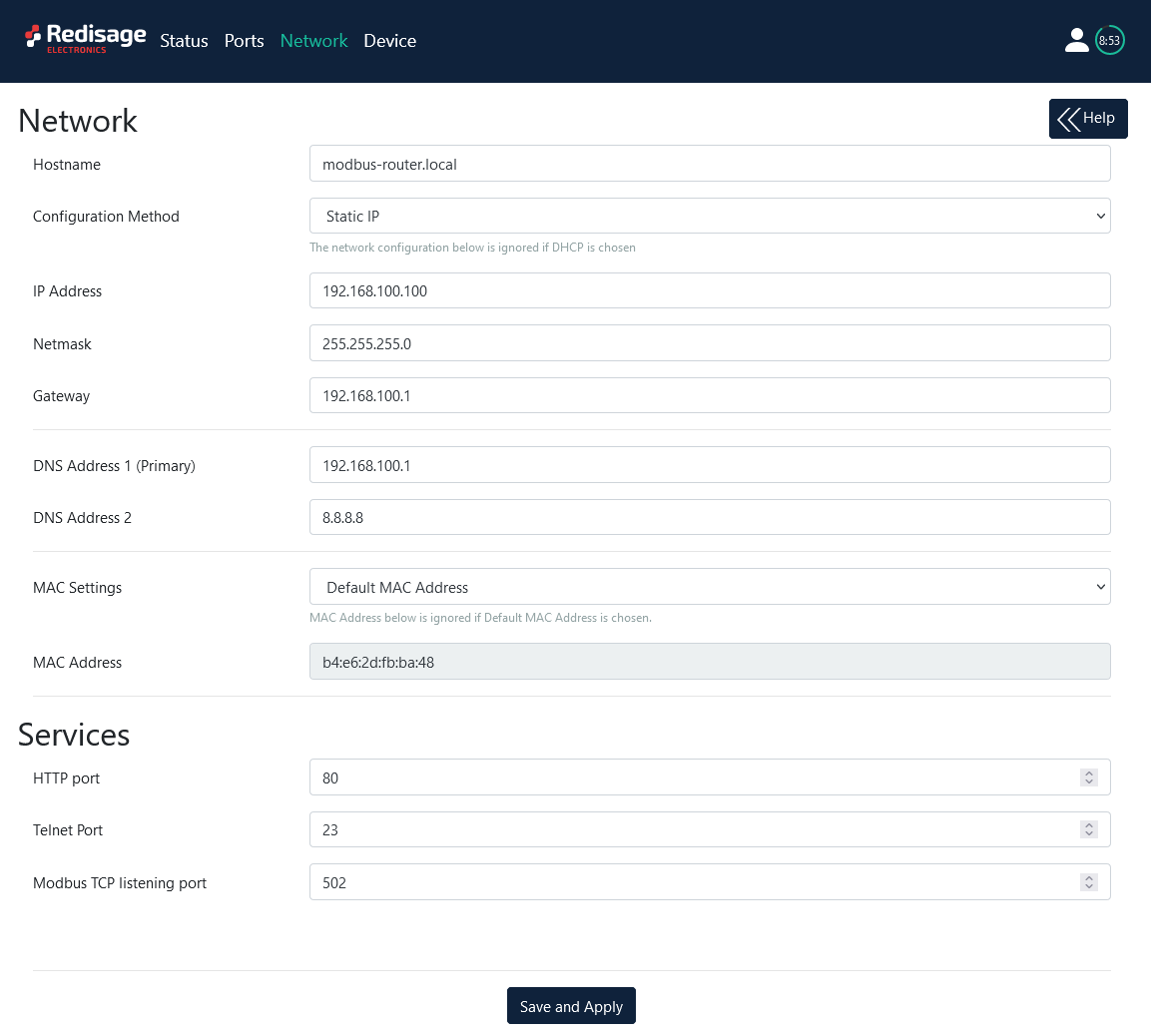
Network settings
IP address of the converter is static by default
It is possible to obtain dynamic IP address. Just switch configuration method from Static IP to DHCP (automatic). This process may cause some issues with identifying converters in LAN unless you have access to the device which is responsible for allocating IP addresses.
Keep in mind that in case of changed IP address you need to type new IP in the address bar and log in again.
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Hostname | Label that is assigned to the Device. |
Configuration Method | Enables/disables the DHCP server. If the DHCP server is disabled, the IP Address of the Device has to be set manually. |
IP Address | IP Address of the Device. |
Netmask | Netmask associated with the IP Address. |
Gateway | Gateway address currently used by the Device. |
DNS Address | Domain Name System used by the Device. |
MAC Settings | Allows setting the default MAC address or typing it manually. |
MAC Address | Allows changing the physical address of the Device. |
HTTP port | Determines the port of the control panel. |
Telnet port | Allows connection with the device via Telnet. |
Modbus TCP listening port | Uses as an entry point for new Modbus TCP connections |
Device page
On the device page there are information about device and tools to factory reset, firmware upgrade and reboot device.
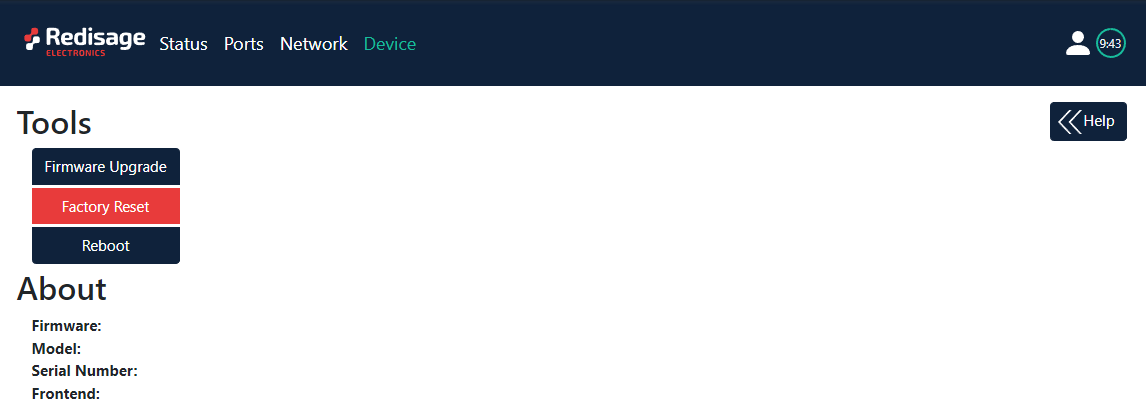
Device page
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Firmware Upgrade | Upgrades firmware |
Factory Reset | Restores default ports settings and default network configuration |
Reboot | Reboots the Device |
About | Contains basic information about the Device |
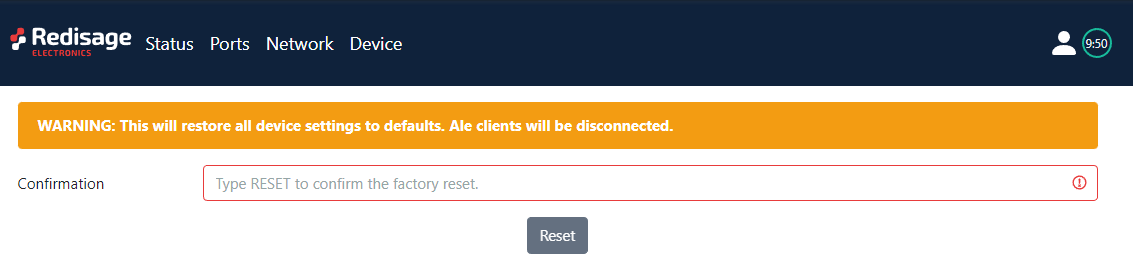
Factory reset
To restore default settings, press the red button. After that, you will be asked for type “RESET”. Then, it takes few seconds for reloading webpage and restarting device.